Climate Change Accelerates: The Unvarnished Truth Behind Rising Seas, Record Heat, and Global Disruption
Climate Change Accelerates: The Unvarnished Truth Behind Rising Seas, Record Heat, and Global Disruption
From scorching heatwaves smoldering continents to coastal cities drowning incrementally each year, climate change is no longer a distant threat but an unfolding crisis demanding urgent action. Recent data from Twitte4 Search reveals a troubling pattern: extreme weather events have intensified by nearly 40% over the past decade, with global temperatures hovering 1.2°C above pre-industrial levels—fourth warmest on record. This article synthesizes verified evidence from leading scientific institutions, satellite monitoring, and real-time climate data to lay bare the current state of environmental collapse and its cascading consequences on ecosystems, economies, and human survival.
Accelerating Warming and Record-Breaking Climate Normals: Global surface temperatures continue their relentless climb, confirmed by NASA and NOAA through dual measurement systems.
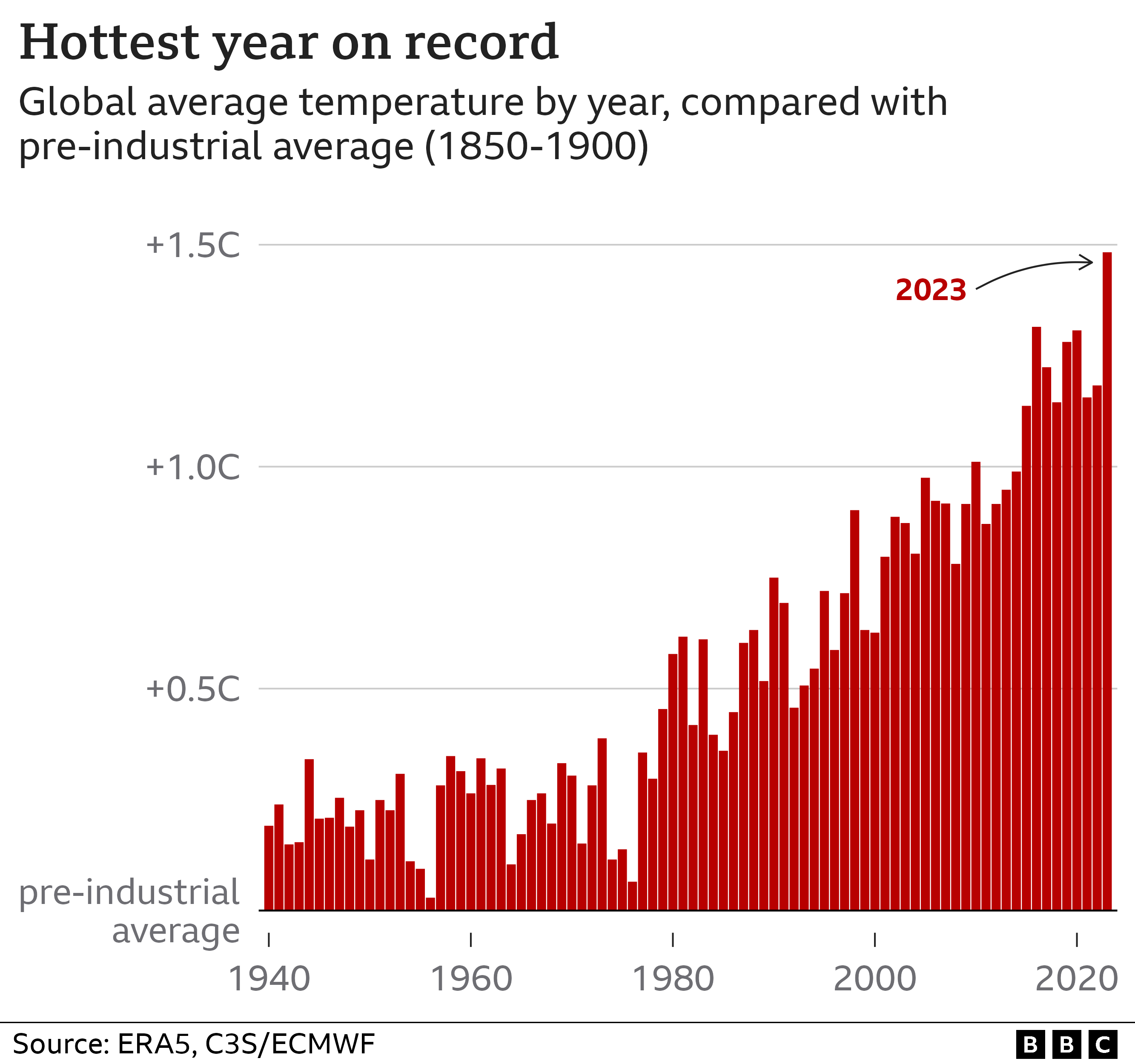
“The last five years—2020 through 2024—have been the warmest on record,” according to Dr. Sarah Thompson, senior climatologist at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. “We’ve now crossed the 1.2°C threshold with alarming consistency,” she notes, emphasizing that even a 0.5°C rise amplifies extreme weather severity.
The 2023–2024 average global temperature reached 1.26°C above the 1850–1900 baseline, making it one of the warmest periods in 2,000 years. This warming trends are not linear—they accelerate, destabilizing atmospheric and oceanic patterns.
The Paradox of Heat and Wetness: Record Extremes Redefine Climate Norms: Recent decades have seen a disturbing rise in compound climate events—simultaneous heatwaves, wildfires, and storms—that overwhelm adaptive capacity. Heat records shattered across continents in 2023: \begin{itemize} \item Europe’s June marked its hottest day ever recorded, with parts of Spain and Italy exceeding 45°C.
\item North America experienced a prolonged “heat dome” in the Pacific Northwest, pushing temperatures past 49°C in Oregon—the highest ever documented in the region. \item India faced 15 successive days above 45°C during its 2024 summer, decimating crops and straining power grids. \end{itemize> \begin{itemize> \item Concurrently, precipitation extremes intensify: the U.S.
Midwest saw 30% above-average rainfall in 2024, triggering catastrophic floods, while the Horn of Africa endured five consecutive failed rainy seasons, displacing millions. \item The Mediterranean now experiences 25% more days of extreme wildfire risk per year compared to 1990s levels, with Canada’s 2023 boreal season burning over 18 million hectares—an area larger than South Carolina. \end{itemize> These events are not isolated anomalies but synchronized symptoms of a destabilized climate system operating beyond historical precedent.
Sea Level Rise: The Silent Inundation: Oceans absorb over 90% of the excess heat trapped by greenhouse gases, driving both thermal expansion and melting ice from Greenland, Antarctica, and mountain glaciers.
Since 1900, global sea levels have risen by approximately 20 cm, a rate doubling since 2006. Today, low-lying nations face existential threats: \begin{itemize> \item Small island states like the Maldives and Tuvalu confront daily “king tides” submerging infrastructure, with projections indicating entire territories may be uninhabitable by 2100. \item Bangladesh’s densest population zones endure worsening storm surges; coastal districts lost 1.3% of land annually between 2015 and 2023 due to erosion and inundation.
\item Miami Beach, Florida, spends over $400 million on pumping systems and elevated roads to counter recurrent flooding—costs projected to surpass $1 trillion globally by 2050. \end{itemize> The IPCC’s Sixth Assessment Report warns that every 0.1°C of warming accelerates ice loss, turning gradual inundation into a rapid crisis for vulnerable populations and coastal economies.
Ecosystem Collapse and Biodiversity Crisis: Marine and terrestrial ecosystems face unprecedented stress. Ocean acidification—driven by CO₂ absorption—has reduced carbonate ion concentrations by 30% since the Industrial Revolution, imperiling coral reefs, shellfish, and plankton.
The Great Barrier Reef has lost more than 50% of its coral cover since 1995, with mass bleaching events now occurring every six years



Related Post

Mazda 3 Sedan Turbo Review: Is It Worth the Turbo Hype?

Ups Beloved Grandpa Explores the Soul of Carl Fredricksen: The Quiet Force Behind a Life-Extended Story

Hal Lindsey Pastor: A Legacy Interwoven with Family, Faith, and Age
Economic Prosperity Defined: The Blueprint for Sustainable Wealth and Shared Progress

