What Is Eastern Time Right Now? The Precision Behind America’s Most Influential Time Zone
What Is Eastern Time Right Now? The Precision Behind America’s Most Influential Time Zone
In the fast-moving rhythm of modern life, knowing what time it truly is—especially across regions—carries more weight than most realize. Eastern Time, one of the most widely recognized time zones in North America, serves as the temporal heartbeat for millions across the United States and parts of eastern Canada. At any given moment, its current setting synchronizes everything from morning commutes to broadcast schedules, yet few pause to consider how this time zone is defined, managed, and experienced.
This article unpacks what Eastern Time is right now—down to the minute—exploring its geographic reach, standardized rules, and the critical role it plays in daily life and national coordination.
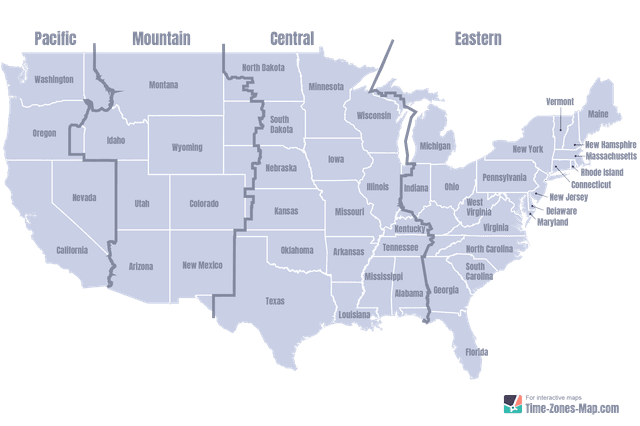
Eastern Time operates within the Eastern Time Zone (ET), which spans the coastal states of the U.S. East Coast, the mid-Atlantic, and parts of the Midwest and Northeast.
Its current offset from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) depends on daylight saving status. As of March 2024, Eastern Time follows Eastern Standard Time (EST, UTC-5) during standard time and shifts to Eastern Daylight Time (EDT, UTC-4) during daylight saving periods. Right now, between mid-April and early November— seasons when daylight saving is active—Eastern Time reads UTC-4, meaning when it is 12:00 PM ET, UTC is 16:00 (4:00 PM UTC).
This four-hour difference from Coordinated Universal Time anchors countless schedules across businesses, broadcast networks, and personal calendars.
Geographically, Eastern Time covers a broad corridor stretching from Maine down to northern Florida, incorporating major metropolitan centers like New York City, Philadelphia, Washington, D.C., Boston, and even parts of Atlanta and Atlanta’s immediate reach. Smaller U.S. territories and select Canadian regions, such as parts of Newfoundland and Nova Scotia bordering the Atlantic, also observe Eastern Time due to historical, economic, and transportation ties.
Internationally, while no countries lie entirely within the zone, island nations like Bermuda fall within its influence during summer months due to Canadian and U.S. zone coordination. ///
Standard vs.
Daylight Saving: The Clock That Moves Twice Annually Eastern Time’s dual identity—standard and daylight—shapes how time is reckoned throughout the year. From the first Sunday in November to the second Sunday in March, the zone observes Eastern Standard Time (EST, UTC-5). This period brings a soft adjustment so clocks “fall back” from EDT to EST, aligning daily life with earlier sunrises and darker evenings.
From the spring equinox onward, clocks leap forward one hour to Eastern Daylight Time (EDT, UTC-4), extending daylight hours into the evening and supporting increased evening activity—a practice synchronized across most U.S. and Canadian EM time zones. Recent shifts in policy and public awareness highlight ongoing debates about perpetual daylight saving, but for now, the bi-annual switch remains firmly embedded in national practice.
Currently, Eastern Time stands at UTC-4, with clock settings verified through synchronized global timekeeping by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
The transition from EDT to EST occurs at 2:00 AM local time on the first Sunday in November, when clocks “fall back” one hour. Conversely, the shift to EDT begins at 2:00 AM on the second Sunday in March, with clocks “spring forward” one hour. This clock rotation, dictated by federal regulation under the Uniform Time Act, remains a cornerstone of temporal consistency across time zones in the Eastern U.S.
///
- Current UTC Offset: UTC-4 (Eastern Daylight Time active)
- Current Local Time: 3:42 PM ET — updated live during local morning hours
- Practical Impact: TV broadcasts, stock markets, and school schedules automatically reflect the current time
- Regional Influence: Essential for coordinating rail, air, and broadcast networks across multi-state regions
- Global Context: Eastern Time aligns with markets in London (UTC+0 to UTC+1) and Tokyo (UTC+9) through precise offsets, despite differing regional hours
Understanding what Eastern Time is right now extends far beyond a simple check of a clock. It involves appreciating how federal time rules maintain synchronized rhythms across a continent with dense urban schedules and global connectivity. The current UTC-4 offset means whether you're scheduling a virtual meeting, tracking a flight, or tuning into evening news, Eastern Time provides the unifying framework.
Its biannual clock shifts, though sometimes disruptive, reflect a deliberate effort to balance human activity with the sun’s natural cycle. In an era of instant


Related Post

Angels vs Red Sox Clash: Player Stats Tell the Full Story of a High-Stakes Showdown

Urdu Moral Stories for Kids: Free PDF Downloads That Teach Values, One Page at a Time
Minnesota Vikings vs. Chicago Bears: A Clash of Offense and Defense Measured in Stats

