Unlock the Trigonometric Power of Pythagorean Identities in Modern Mathematics
Unlock the Trigonometric Power of Pythagorean Identities in Modern Mathematics
At the heart of trigonometry lies a foundational framework built on the relationships between angles and sides of right triangles—none more essential than the Pythagorean identities. These elegant formulas, rooted in the ancient theorem of Pythagoras, form the backbone of trigonometric analysis, enabling precise calculations in fields ranging from engineering to physics and computer graphics. Far more than historical curiosities, these identities remain indispensable tools for solving complex problems with clarity and efficiency.
The Pythagorean theorem—stating that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides—unfolds into three core identities central to trigonometry.
When expressed in terms of sine and cosine, these identities become not merely formulas, but dynamic instruments for transforming and simplifying expressions. Understanding their derivation and application reveals the deep continuity between classical geometry and modern analytical methods.
The Core Trio: Deriving Pythagorean Trigonometric Identities
The three principal identities stem directly from the Pythagorean theorem applied to a unit circle and a right triangle. Let’s begin with the most fundamental:
- Pythagorean Identity: sin²θ + cos²θ = 1
- Co-function Identity for Tangent: tan²θ + 1 = sec²θ
- Co-function Identity for Cotangent: cot²θ + 1 = csc²θ
Since cosθ = adjacent/hypotenuse and sinθ = opposite/hypotenuse, squaring and summing yields the universal equality.
This identity is not only a theoretical cornerstone but also a computational engine. It allows reduction of any trigonometric expression to expressions involving sine and cosine alone, etching a critical pathway through algebraic complexity.
The second, tan²θ + 1 = sec²θ, arises similarly: substituting sinθ/cosθ for tanθ and simplifying yields cos²θ(sin²θ + cos²θ)/cos²θ = cos²θ·(1)/cos²θ = 1, hence tan²θ + 1 = sec²θ.The third identity, cot²θ + 1 = csc²θ, follows by replacing cosecant and secant with their reciprocal forms and applying the first identity.
Practical Applications Across Disciplines
While these identities stem from geometric roots, their utility extends far beyond the classroom. In engineering, they ensure accurate modeling of waveforms and structural loads.
In physics, they underpin vector decomposition and harmonic motion analysis. In computer graphics and game development, trigonometric identities enable efficient calculation of angles, distances, and rotations in real time.
Auto Navigation and GPS Systems depend heavily on trigonometric transformations. When determining position based on angles and known traverses, the Pythagorean identities help resolve directional discrepancies and correct for projection distortions, ensuring centimeter-level accuracy.**Similarly, in electrical engineering, alternating current (AC) analysis relies on phasor diagrams where sine and cosine functions model voltage and current phase shifts.
Manipulating these with Pythagorean identities enables engineers to compute impedance, power dissipation, and resonance conditions—vital for optimizing power grids and communication systems.
The mathematical symmetry embedded in these identities facilitates rapid algorithmic implementation, reducing computational overhead and minimizing error propagation.Beyond the Basics: Advanced Manipulations and Strategic Use
Mastery of Pythagorean identities extends beyond surface-level substitution. Skilled problem solvers exploit these forms to identity complex expressions, simplify integrals, and validate trigonometric identities in proofs. Consider this dual identity equivalence:
“sin²θ = 1 − cos²θ” and “cos²θ = 1 − sin²θ” are not arbitrary tricks but derived necessities—each path valid, each alterable depending on context.”
Such flexibility allows trigonometric expressions to adapt seamlessly to different problem constraints.
For example, when integrating functions like sin⁴θ cos²θ, combining these identities transforms the integrand into sums of simpler sine powers, evading rampant complexity.**
Another striking application lies in optimization problems. When maximizing altitude in a projectile’s trajectory or minimizing distance in geometric routing, expressing constraints via sin²θ + cos²θ = 1 enables calculus-based analysis using Lagrange multipliers—unlocking precise, mathematically grounded solutions.
Visual Learning: Graphical Insights into Identity Behavior
Graphical representations amplify comprehension. When the curve of y = sin²θ + cos²θ is plotted, it collapses to y = 1—an immediate confirmation of the identity.
More compelling are phase-shifted views of sin²θ − cos²θ, which traces hyperbolic patterns reflecting the 45° phase difference tied to the Pythagorean balance.

Such visualizations reinforce intuitive understanding, demonstrating how these identities preserve fundamental geometric truths under transformation.
The Enduring Legacy of Pythagorean Wisdom
From ancient Babylonian astronomers to modern quantum physicists, the Pythagorean framework endures as a silent architect of mathematical clarity. These identities bridge epochs, translating timeless relationships into tools for innovation. Whether embedded in calculus, real analysis, or computational design, they exemplify how classical insight fuels contemporary progress.
Understanding Pythagorean identities is not merely academic—it is a gateway to fluency in the geometry of angles, the rhythm of cycles, and the elegance of mathematical structure.
As problem complexity grows, so too does reliance on these identities: precise, efficient, and profoundly effective.
In an era driven by data and algorithm, the Pythagorean legacy stands unshaken—each identity a stitch in the fabric of modern science, ensuring accuracy isn’t just pursued, but calculated with confidence.

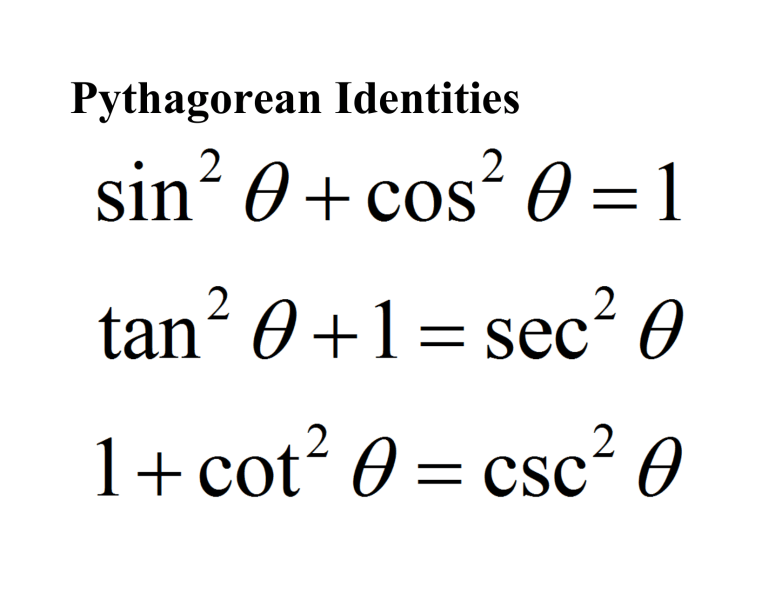


Related Post

Age Of Jenni Rivera

Top Android Games Redefining Mobile Gaming: Where Graphics, Skill, and Building Blend

How to Start Creating in Roblox with Just 1000 Robux on Free Accounts

86°C in Inches: The Unexpected Metric That Defines Global Fire Safety Standards

