Under the Microscope: The Layered Architecture of Cardiac Muscle and Its Functional Mastery
Under the Microscope: The Layered Architecture of Cardiac Muscle and Its Functional Mastery
Beneath the visible elegance of the human heart lies a sophisticated microstructure—cardiac muscle organized into distinct, precisely layered arrangements that enable sustained, rhythmic contractions essential for life. Far more than mere tissue, the layered anatomy of myocardial fibers underpins the heart’s ability to pump blood efficiently, contract with precision, and endure relentless cyclic stress. Understanding the layered composition—comprising endocardial, myocardial, and epicardial strata—reveals how structural organization directly influences electrophysiological function and clinical resilience.
This layered architecture is not just a biological curiosity; it is the blueprint of cardiac durability and performance, shaping everything from electrical conduction to mechanical force generation. The heart’s outer layer, the endocardium, forms a thin, continuous seam lining the inner chambers and valveless chambers. Composed primarily of a single layer of simple endocardial cells—flat, flattened myocytes beneath a thin basement membrane—this layer provides a smooth, low-resistance surface critical for unhindered blood flow.
"The endocardium acts as both a protective barrier and a dynamic interface, minimizing turbulence while supporting the integrity of chamber walls," notes Dr. Elena Marquez, cardiac histologist at the Cardiovascular Research Institute. Beneath this lies a delicate subendocardial layer rich in capillaries and fibroblasts, supplying nutrients and anchoring the muscle to the endocardial framework—vital for maintaining structural cohesion during repetitive contractions.
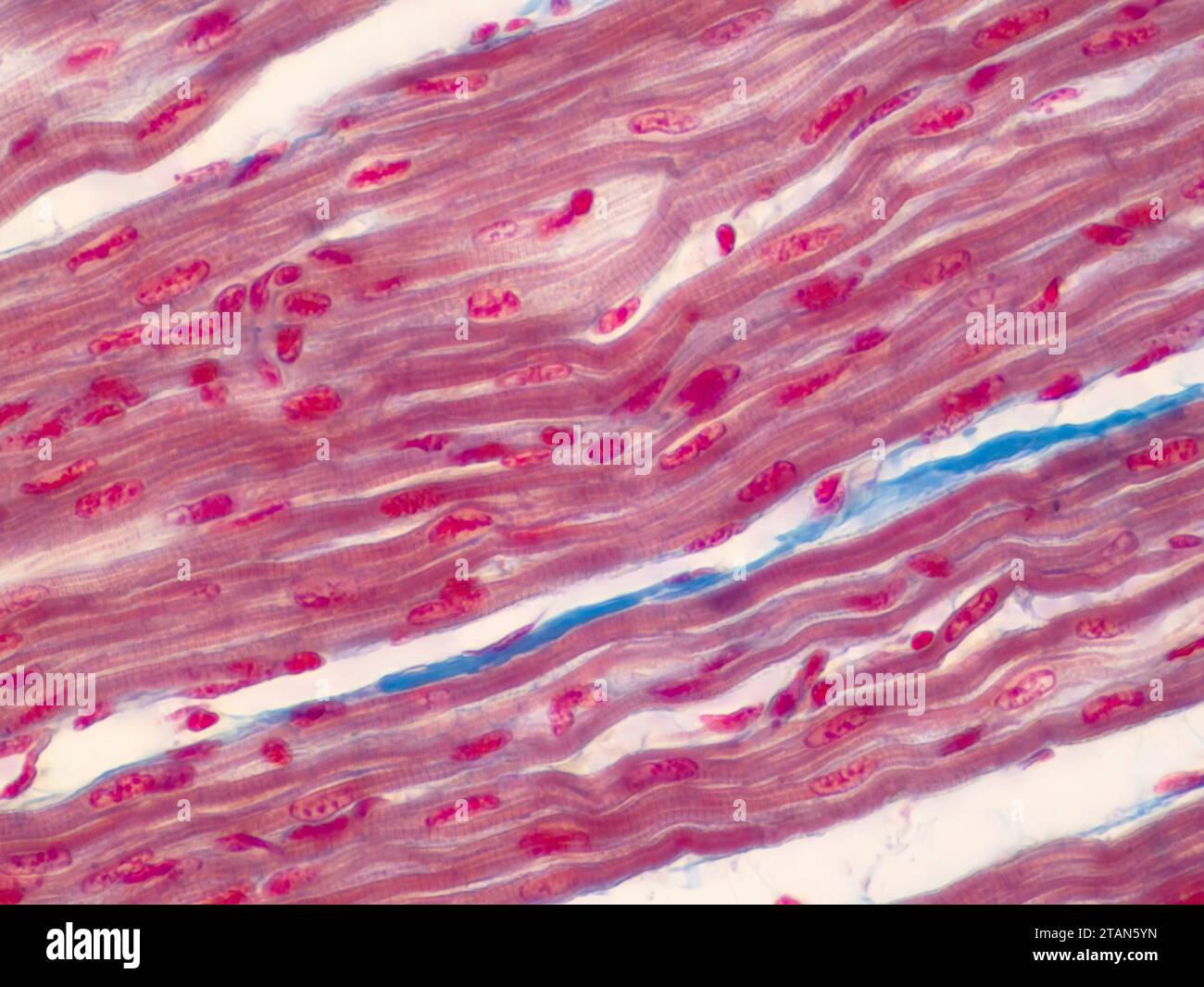
Beneath the endocardium, the myocardial layer dominates the heart’s volume, forming a dense, cellular matrix that constitutes the majority of cardiac muscle mass. This middle stratum is where the heart’s contractile power resides, assembled in a distinctive helical pattern of myofibers. Each myocardial fiber is a multinucleated cardiomyocyte—typically 15–30 µm in diameter—extending greater than 25 cell lengths, creating a highly interconnected network.
This architectural design maximizes mechanical efficiency: the spiral orientation, often described as “interpenetrating bundles,” allows fibers to contract in coordinated waves, propelling blood forward with remarkable coordination. The dense cytoplasm houses abundant mitochondria—often 5–10% of the cell volume—reflecting the high metabolic demand of continuous cardiac work. The helical arrangement follows a region-specific blueprint: in the right ventricle, fibers interlace mostly in the circumferential plane, while the left ventricle exhibits a complex corkscrew pattern optimizing both force generation and filling dynamics.
This spatial organization ensures directional force transmission, with longitudinal and radial contraction components working in concert. “It’s a marvel of biological engineering,” explains Dr. Marquez.
“The myocardial layer doesn’t just contract—it coordinates. Every fiber’s orientation is tuned to optimize pumping efficiency, turning electrical signals into mechanical power.” The dense extracellular matrix, dominated by collagen threads and elastin, further supports this layered integrity, acting as both scaffold and signaling conduit between cells. Beneath the myocardial layer lies the epicardium, the heart’s outermost visceral layer—originally a layer of simple squamous epithelium now largely replaced by connective tissue and adipocytes, with sparse myocytes and rich vasculature.
Though less metabolically active, the epicardium plays a crucial role in regeneration and repair. Its surface harbors coronary arteries and nerves, branching from the aorta to supply the myocardium itself. Beneath this lies the subepicardial layer, containing fibroblasts and progenitor cells capable of activating during injury, though less so than embryonic or postnatal stem cell reservoirs.
“The epicardium is more than a protective wrapper,” notes Dr. James Holloway, cardiothoracic pathologist. “It’s a reservoir of regenerative potential, influencing how the heart responds to stress and disease.” The interplay between these three layers—endocardium, myocardium, and epicardium—forms a layered functional cascade essential for cardiac performance.
The myocardial layer’s helical myocyte architecture maximizes contractile coordination, enabling the heart to generate pressure gradients exceeding 100 mmHg during systole and maintain diastolic relaxation necessary for ventricular filling. The stratified structure also facilitates efficient electrical propagation: action potentials spread rapidly through the cell interconnections, supported by gap junctions enriched in connexin 43, ensuring synchronous contraction across vast myocardial sheets. Clinically, disruptions to the layered organization profoundly impact cardiac function.
Endocardial damage—seen in infections like rheumatic heart disease—compromises surface smoothness, increasing thrombosis risk and reducing pumping efficiency. Myocardial disorders such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy feature disorganized myofiber alignment, impairing contraction and leading to arrhythmias. Epicardial inflammation in myocarditis disrupts structural integrity, weakening contractions and predisposing to scarring.
Even surgical interventions, like valve repairs, must respect these layers to preserve native architecture and function. The layered design of cardiac muscle is not merely a structural curiosity; it is the foundation of the heart’s lifeblood. From the thin, streamlined endocardium to the densely packed helical myocardium and the reparative epicardium, each stratum fulfills a distinct yet interdependent role. This layered complexity allows the heart to endure the relentless demands of life—contracting



Related Post

Unlocking the Power of MolarMassOfOxygen: The Foundation of Chemistry and Life

Bolly4u Movie Punjabi: Your Ultimate Guide to India’s Vibrant Punjabi Cinema

AllMoviesHub HD: Your Ultimate Destination for Ultra-High-Quality Movies Online

Find Song Lyrics Instantly with the Power of Vault.Nimc.Gov.Ng

