Mm To Cm
Mm To Cm: When Medical Imaging Shifts from Millimeters to Centimeters — How Transformational Scale-Shifts Are Redefining Healthcare Precision
In the evolving landscape of medical diagnostics, the conversion from millimeters (mm) to centimeters (cm) represents far more than a mere unit transformation—it signals a fundamental shift in how clinicians interpret and operationalize spatial data within the human body. Though seemingly technical, this conversion underpins critical decisions in imaging accuracy, treatment planning, and patient outcomes. Translating structural details from sub-millimeter clarity to broader, anatomically contextualized views demands more than simple arithmetic: it requires an understanding of scaling principles, clinical relevance, and technological integration.From radiography to MRI, this transformation from mm to cm unlocks accessibility without sacrificing diagnostic fidelity, bridging microscopic detail and macro visibility across medical imaging modalities. The practical implications of converting mm to cm are profound, directly influencing how medical professionals assess abnormalities, plan surgeries, and monitor disease progression. While a millimeter represents a thousandth of a centimeter—just 0.1 cm—this seemingly minor unit boundary carries outsized significance in clinical context.
Consider a bone fracture measured at 3.2 mm versus 0.32 cm; though mathematically equivalent, the perceived scale affects confidence in detection and intervention urgency. Healthcare providers rely on this conversion to standardize measurements, avoid miscommunication, and ensure consistency across imaging reports. This process also enhances patient comprehension, as translating precise data into clinically meaningful metrics fosters clearer discussions about injury severity and recovery timelines.
The Scale Transformation: Precision at a Crossroads
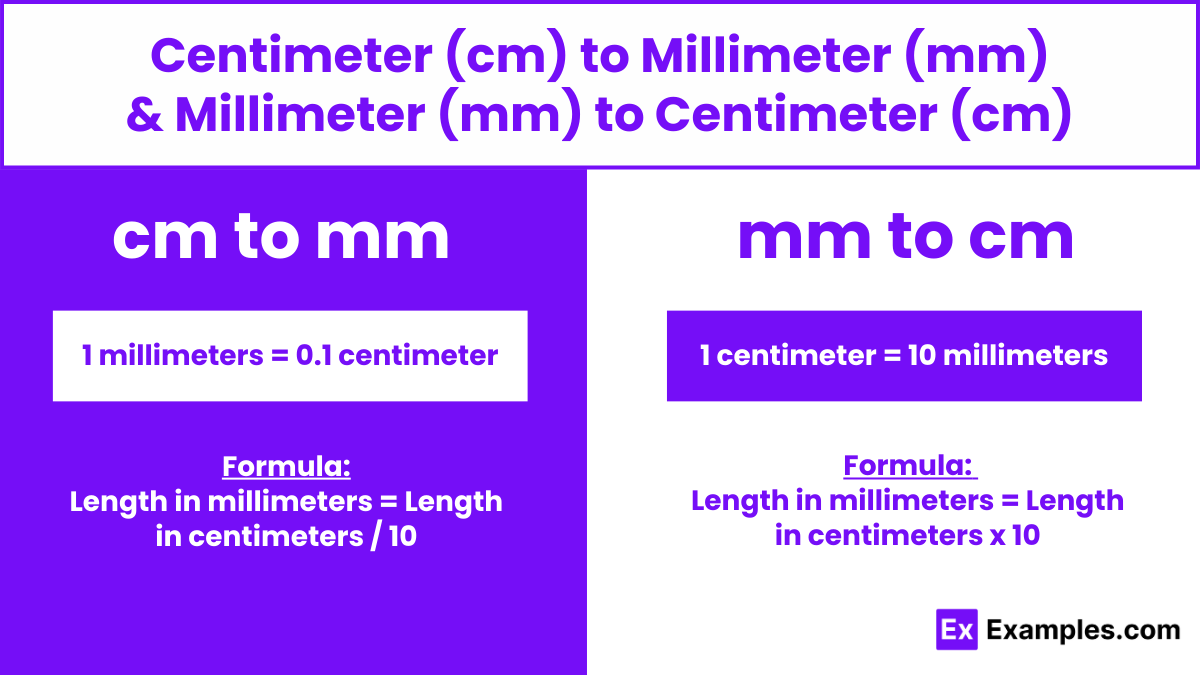
At the core of the mm to cm transition lies a simple mathematical relationship—but in medical imaging, this conversion anchors entire frameworks of measurement and interpretation. One centimeter consists precisely of 10 millimeters, a fixed ratio that ensures consistency across platforms and practices. This exact conversion enables the harmonization of data from diverse sources, including X-rays, CT scans, ultrasounds, and digital pathology systems, most of which report at the centimeter level for clinical readability.Yet, the clinical value of this scaling extends beyond numerical equivalence. When imaging identifies a tumor lesion merely 1.5 mm in diameter—equivalent to 0.15 cm—sudden scale shift elevates a sub-surface detail into a diagnostically actionable finding. Radiology departments routinely use such conversions to contextualize findings within normative anatomical dimensions.
For instance, a pulmonary nodule 8 mm across translates not just to 0.8 cm, but to a size prompting close radiological surveillance based on well-established thresholds. These interpretive thresholds depend on accurate metric translation, underscoring why mm-to-cm conversion is not purely technical—it is diagnostic logic in action.
Applications Across Imaging Modalities
Different imaging technologies leverage mm-to-cm conversions in unique, specialized ways, each optimizing precision for specific diagnostic needs.- **Radiography and CT Imaging:** X-rays and computed tomography deliver high-resolution grayscale maps where a 1 mm shift can differentiate viable tissue from pathology. In CT scans, where axial slices measure cubic centimeters, converting fine millimeters to centimeters allows for accurate volumetric analysis—critical in monitoring tumor response or assessing bone density changes over time. A 2 mm shift in spinal curvature, for example, may equate to a several percent volume difference, prompting timely intervention.
- **Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):** MRI excels in soft tissue contrast but requires precise co-registration across scans. Converting mm-scale detail—such as a small meniscal tear in a knee image—to cm ensures compatibility with anatomical atlases and surgical planning systems. Here, 3.5 mm lesions become meaningful when contextualized as 0.35 cm, enabling clinicians to map exact positions within 3D anatomical frameworks used for navigation and biopsies.
- **Ultrasound and Doppler Studies:** In obstetrics and vascular imaging, mm-to-cm conversion supports real-time assessment of fetal growth or blood flow dynamics. A fetal head circumference measured at 3.8 cm (equivalent to 38 mm) guides developmental monitoring against standardized growth curves, where cumulative scale differences determine clinical significance across gestation. Each modality intricately weaves mm-to-cm translation into its operational logic, proving that accurate scaling is not ancillary—but foundational to diagnostic integrity.
The Human Impact: From Data to Diagnosis
Beyond imaging software and radiological interpretation, the conversion from mm to cm touches patient care at the human level. Clinicians rely on this scaling to communicate risk, track recovery, and tailor therapies with confidence. Imagine comparing a skin lesion’s diameter: “The crust measures 0.9 mm” versus “It expands to 9 mm”—both accurate in mm, but the latter frames a progression of interest far more compellingly for patients and physicians alike.Moreover, standardized mm-to-cm reporting enhances interoperability across electronic health records (EHRs), where dimensional consistency prevents errors in longitudinal tracking. When a patient’s liver tumor budgeted at 5.4 mm in 2023 evolves to 0.54 cm in 2024, that quantifiable accuracy shows clear improvement—or regression—without ambiguity. Such precision supports informed consent, guides surgical margins, and aligns treatment protocols with measurable benchmarks.
In rare diseases affecting growth—such as osteogenesis imperfecta—mandatory mm-to-cm translation transforms subtle bone fragility into quantifiable severity. Pediatricians and orthopedic specialists depend on this clarity to adjust medications, surgery timing, or physical therapy intensity, always anchored in precise, clinically validated metrics.
Across imaging technologies and clinical workflows, the humble conversion from millimeters to centimeters emerges as a quiet but indispensable pillars of precision medicine.
By anchoring sub-millimeter detail within the comprehensible centimeter framework, healthcare transforms data into diagnosis, and data into action—ultimately advancing patient outcomes one precise scale at a time.


Related Post

Navigating Insurance: Common Problems & Smart Solutions That Save Time, Money, and Stress

Soaking Mormons: The Transformative Power of Immersive Allegiance — Unleashing Spiritual Renewal and Community Depth

Watch It TV Series Net: Your Ultimate Directory to Binge-Worthy Actions and Awards

Bring Back the Golden Era: Reviving Old League Masteries Through Mods and Dark-Coded Craftsmanship

