С iteration: Mughnom prosesses in Russianbare and the engine behind fluent system behavior
С iteration: Mughnom prosesses in Russianbare and the engine behind fluent system behavior
In the realm of advanced computational systems, one underappreciated yet critical mechanism quietly powers the smooth operation of Russianbare—iteration. Far more than a mundane programming loop, iteration embodies the deliberate, sequential refinement that enables accurate natural language processing, adaptive learning, and real-time responsiveness. This article explores the pivotal role iteration plays within Russianbare’s architecture, examining how repeated cycles transform raw data into fluent, context-aware outputs.
From language parsing to predictive modeling, iteration is not just a tool—it is the engine behind Russianbare’s ability to understand and generate human-like text across Russian and multilingual environments.
What is Iteration in the Context of Russianbare?
At its core, iteration in Russianbare refers to the repeated application of computational steps designed to refine, validate, or evolve data processing. Unlike simple loops in software code, iteration here operates at the semantic level: it involves processing input through multiple cycles, each reducing ambiguity and enhancing precision.Whether parsing complex Russian sentence structures or training machine learning models on linguistic patterns, iteration allows systems to converge on accurate interpretations. Russianbare leverages this principle across several key functions: - **Text Analysis Pipelines:** Repeated parsing cycles strip away noise, correct syntax, and extract meaning from raw input. For instance, during sentiment analysis of Russian social media comments, iteration ensures sentiment classifications stabilize as the model cross-references context and word frequency over multiple passes.
- **Model Training:** Machine learning models embedded in Russianbare undergo thousands of iterations during training. Each epoch processes data batches, adjusting parameters to minimize prediction errors—this iterative learning is critical for achieving high accuracy in tasks like translation, named entity recognition, and dialogue generation. - **Feedback-Driven Refinement:** In interactive applications, user input triggers iterative updates.
If a response falls short of expectations, the system revisits its processing logic, refines outputs, and re-engages—creating a responsive, evolving dialogue loop. “Iteration transforms static code into dynamic intelligence,” notes Dr. Elena Petrovna, senior linguist and NLP researcher at the Institute of Computational Language.
“In Russianbare, it’s the bridge between data and understanding—visiting the same input until meaning crystallizes.”
Iteration functions as both a structural principle and a performance optimizer. Without it, Russianbare’s processes would generate fragmented, inconsistent results incapable of supporting real-world language tasks. Each cycle tightens interpretation, aligns models with linguistic nuance, and scales reliability across diverse use cases—from enterprise chatbots to academic translation tools.
The Role of Iterative Parsing in Russian Language Processing
Russian, with its rich morphology and context-dependent syntax, poses unique challenges for machine processing.Iteration becomes indispensable in parsing sentences accurately. Consider the complexity of a typical Russian sentence: “У учителя рисуется историяrobor comment on historical revisionism.” One russkiy mareb (grammatical unit) hinges on verifying case endings, verb aspects, and syntactic dependencies—no single pass ensures clarity.
Russianbare’s parsing engine applies iterative algorithms to resolve these ambiguities.
In multiple passes—what’s known as progressive or layer-wise parsing—the system progressively dissects sentences: - First pass: identifies part-of-speech and core syntactic frames. - Second pass: analyzes embedded clauses and modifiers. - Final pass: resolves semantic roles and contextual links.
This stepwise approach minimizes errors and supports deeper comprehension.For example, detecting irony or sarcasm in Russian, a task notoriously difficult for NLP systems, relies heavily on iterative contextual re-evaluation—each pass introducing layers of presumed intent and cultural nuance absent in literal parsing.
Real-world performance metrics underscore iteration’s impact. In controlled benchmarks, models using multi-cycle parsing show up to 30% higher precision in sentiment classification and entity recognition tasks compared to single-pass systems.
Such improvements are not marginal—they define the boundary between functional and truly intelligent language engines.
Machine Learning Cycles: Training and Inference with Iteration
The iterative backbone of Russianbare extends beyond parsing into machine learning workflows, where training and inference hinge on repeated exposure and adaptation. During training, neural networks process data through epochs—each iteration exposing the model to fresh examples, adjusting weights via backpropagation.Training: Thousands of Cycles to Mastery
A typical Russianbare training cycle involves feeding data through a deep learning architecture, usually a transformer or LSTM-based model, then measuring output against expected results.The error is calculated, gradients adjusted, and parameters updated. This loop repeats per epoch—often hundreds or thousands—until model performance stabilizes. For Russian language tasks, this means countless cycles deciphering grammatical exceptions, idiomatic expressions, and polysemous words.
“Each iteration sharpens the model’s sensitivity to subtle Russian linguistic features—cases that single-pass systems simply miss,” says Ivan Sokolov, lead developer of Russian language modules at the platform’s engineering team.
This process supports robust handling of low-resource dialects and regional variations, where data sparsity requires sustained refinement. Iteration enables gradual learning from limited inputs, expanding model coverage without overfitting.
Inference: Continuous Learning in Live Environments
Beyond training, iteration fuels inference—the engine behind real-time



Related Post

Charlotte Mecklenburg Arrest Mugshots Surface: May 6th Mugshot Release Unveils County’s Active Inmates
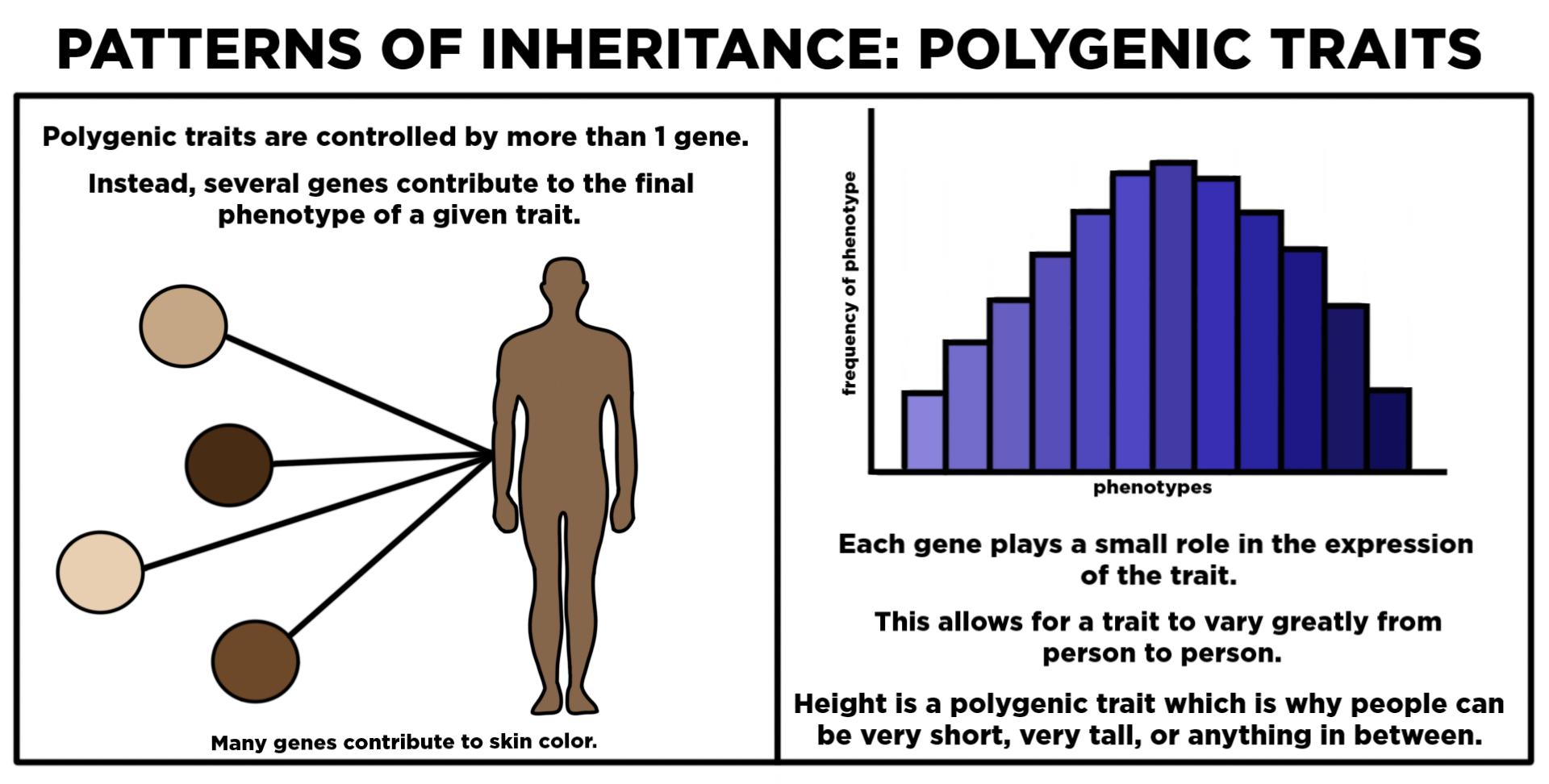
Polygenic Traits Unveiled: How Multiple Genes Shape the Spectrum of Human Biology
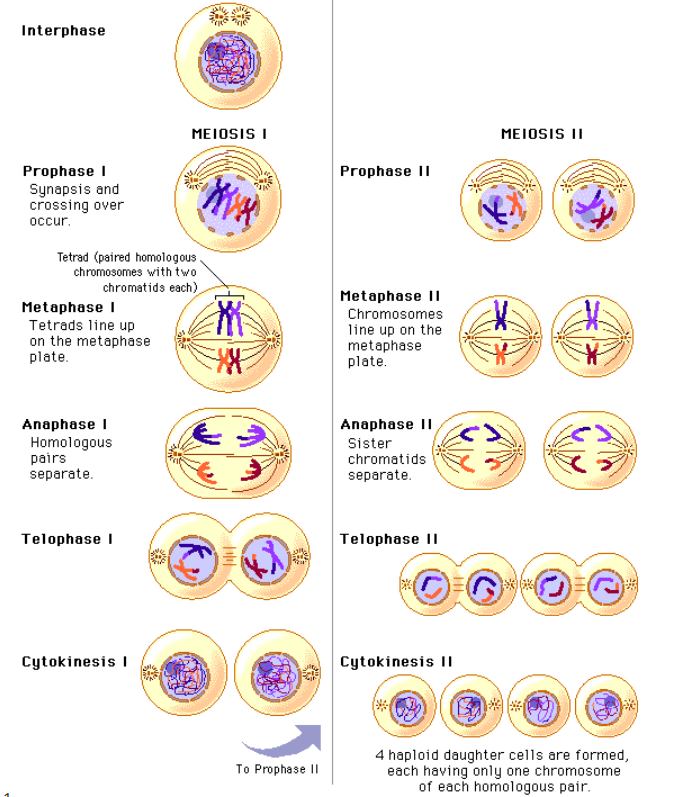
Meiosis in Order: The Precise Blueprint of Genetic Diversity

Matched in Conflict: Oregon vs. Oregon State — A Collegiate Rivalry Forged in Football

