Install Python Libraries in Azure Databricks: Your Essential Step-by-Step Guide
Install Python Libraries in Azure Databricks: Your Essential Step-by-Step Guide
Azure Databricks has emerged as a powerful platform for data engineering, machine learning, and collaborative analytics, enabling teams to build scalable, cloud-native workflows. A fundamental capability that empowers data professionals on this platform is the seamless installation of Python libraries—critical for transforming raw data into actionable insights. This guide delivers a precise, no-nonsense walkthrough on integrating Python libraries into Databricks workspaces, eliminating ambiguity around setup and ensuring immediate usability.
Azure Databricks, built natively on Apache Spark, provides integrated support for Python scripts through scripts, Notebooks, and custommat評als. But to unlock Spark’s full potential—especially when working with pandas, scikit-learn, TensorFlow, or other industry-standard libraries—developers must install the correct Python environments. Unlike local setups, Databricks operates in a shared, managed workspace where dependency management and environment consistency directly impact efficiency and deployment reliability.
Why Python Library Management Matters in Databricks
The ability to install and manage Python libraries effectively underpins nearly every analytical project in Databricks.Whether deploying a machine learning model, running ETL pipelines, or analyzing petabytes of data, the correct library ecosystem ensures performance, compatibility, and reproducibility. Unlike traditional frameworks, Databricks’ cloud-native architecture demands deliberate setup: pre-installed libraries, optimized dependency resolution, and version control to prevent “works on my machine” pitfalls.
Databricks supplies a standard base image preloaded with essential tools, but users rarely rely solely on defaults. Customizing the environment to include domain-specific libraries—such as PySpark for distributed data processing, XGBoost for gradient boosting, or Hugging Face Transformers for NLP—requires a clear method to inject packages programmatically.
Step-by-Step: Install and Integrate Python Libraries
Begin by launching your Databricks workspace and opening a Notebook or script interface.While Databricks notebooks support inline commands, structured script installations via configuration files or require a controlled environment—ideal for larger teams or production pipelines.
To install Python libraries in Databricks, leverage pip in a script or notebook cell. While basic `!pip install library-name` works, best practices recommend wrapping this in a script or using Databricks’ deployment mechanisms for version consistency.
For example, to install pandas and scikit-learn in a new Python notebook:
```python import pandas as pd import scikit-learn|| ```
For projects requiring additional dependencies—such as TensorFlow or PyTorch—specify versions to avoid conflicts. A reliable approach is to define a requirements.txt file and use:
```bash pip install -r requirements.txt --extra-index-url https://pypi.azuredatabricks.net/ ```
Note the strategic use of the Azure Databricks-specific module index URL, which enhances package availability and security by routing downloads through Databricks’ internal repositories.
Using Official Databricks Libraries and Community Ecosystems
Databricks maintains a curated set of community-backed libraries optimized for Spark and distributed computing. Libraries like miracle (for PySpark dev), pyspark.sql.functions, and even integrations with MLflow or Kubeflow are included by default or can be added with:```python from pyspark.sql.functions import col, floor ```
For machine learning workflows, installing TensorFlow or PyTorch directly via pip supports GPU-accelerated training within Databricks clusters.
When integrating custom libraries, validate compatibility with Spark’s execution model—some packages may require careful configuration to avoid breaking distributed operations. For instance, NumPy works well in single-node environments but requires ring mode in notebooks via `%pyspark.mode shown as `I/O` but `EVAL` with `environment` settings.
Adopting version pinning—e.g., `pip install pandas==1.5.3 scikit-learn==1.3.0`—ensures predictability across runs and prevents unexpected behavioral shifts due to library updates.
Best Practices for Environment Consistency
Use version-controlled dependencies: Publish requirements files in source control and version them alongside notebooks to ensure reproducibility across clusters and teams.
Leverage Databricks environments: Define dedicated environments (Dev, Test, Prod) with standardized library sets to isolate production dependencies from development workflows.
Audit library compatibility: Verify whether a library supports PySpark or can be used in distributed contexts—some Python-native tools have limited or no Spark compatibility.
Monitor inventory using Databricks features: Use Databricks Workspace Inventory to track installed packages, detect drift, and automate dependency updates.
Teams should also consider ephemeral setup workflows: generating and sharing NOTE books or scripts that define library needs, reducing set Yourself Time and onboarding friction. Automating library installation through CI/CD pipelines—especially in GitOps workflows—further solidifies reliability.
Real-World Example: Building a Python Notebook with Core Libraries
Consider a data analysis task requiring pandas for data manipulation, scikit-learn for model training, and matplotlib for visualization—all within Databricks notebooks.Here’s a typical setup:
- Start with a base Python notebook: ```init Notebook; import pandas; import numpy; from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression; import matplotlib.pyplot as plt; `
- Add required libraries via pip with pinned versions: ```%pip install pandas==2.1.3 scikit-learn==1.3.0 matplotlib==3.8.1 `
- Write a script to load, preprocess, and visualize data: ```python ```python import pandas as pd from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score df = pd.read_csv("s3://my-bucket/processed-data.csv") X = df[["feature1", "feature2"]].values y = df["target"].values X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2) model = LogisticRegression().fit(X_train, y_train) preds = model.predict(X_test) accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, preds) print(f"Model accuracy: {accuracy:.2f}") plt.scatter(X_test[:,0], y_test, color="blue", label="Actual") plt.scatter(X_test[:,0], preds, color="red", label="Predicted") ```
842This compact but comprehensive snippet demonstrates how to integrate essential Python libraries into a functional, production-ready notebook. By combining pip dependency management with Databricks’ distributed computing foundation, teams can rapidly prototype and deploy data science workflows at scale.
Choosing the right library versions, avoiding whitespace in dependency lists, and testing environment consistency are critical. Teams that master Python library installation in Databricks gain not just convenience—but control, reproducibility, and scalability.
The Future of Python in Azure Databricks
As Databricks continues to unify data and AI workflows, the integration of Python libraries remains a cornerstone capability.With growing advancements in distributed ML, real-time processing, and interactive analytics, Python’s role deepens. Next-generation tooling—such as optimized Spark-native Python bindings and tighter MLflow integration—further simplify library deployment and monitoring. For organizations leveraging Azure Databricks, mastering Python library setup is not optional: it’s essential to harness the full power of cloud-scale data platforms effectively.
In summary, installing Python libraries in Azure Databricks is a foundational, repeatable process that combines simplicity with professional rigor. By following best practices—version pinning, environment isolation, automated dependency management—teams ensure stable, scalable, and collaborative workflows. Whether beginner or expert, understanding this workflow empowers faster innovation and reliable data-driven outcomes.



Related Post
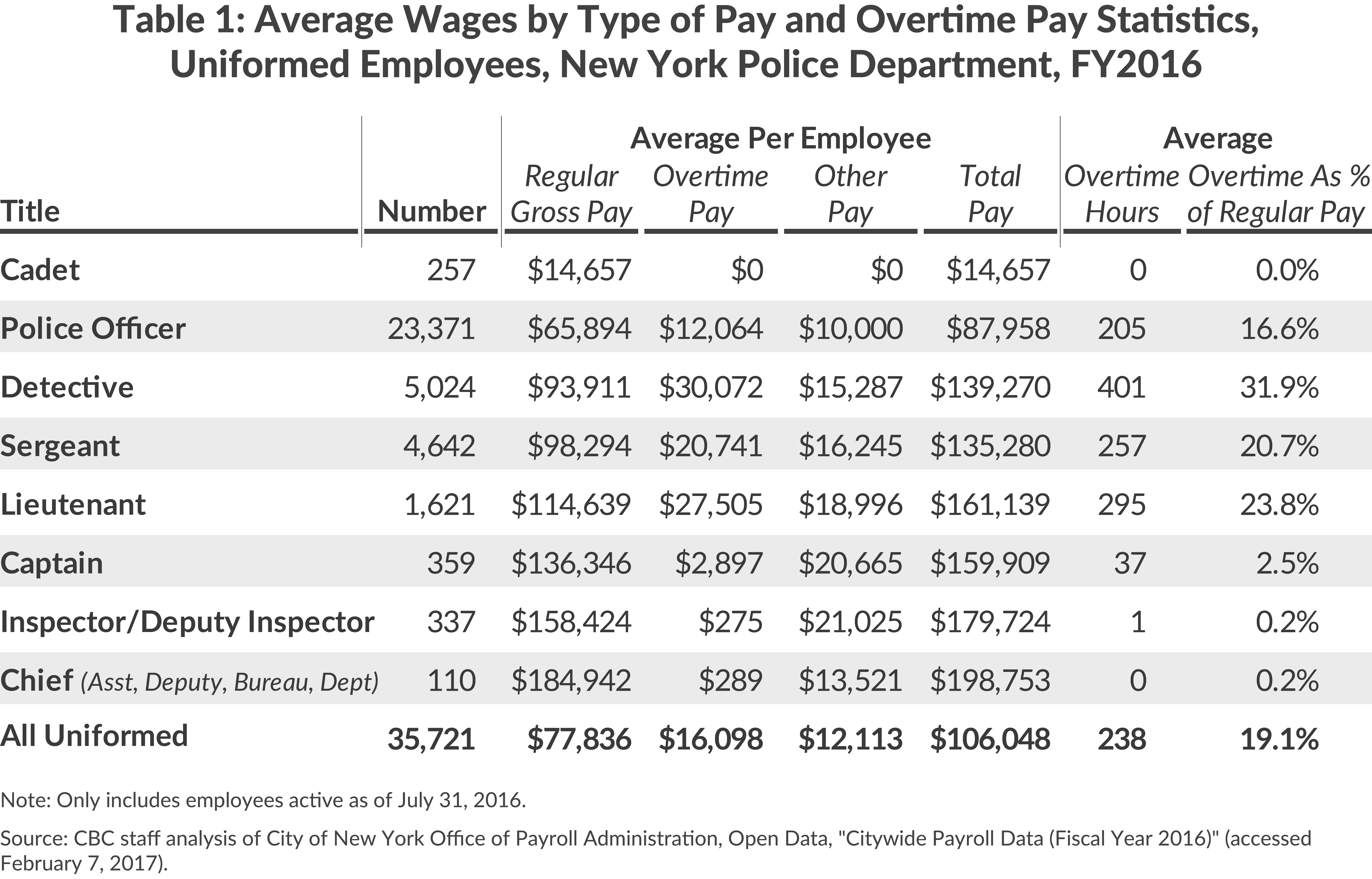
At a Glance: Decoding the NYPD Salary Scale with the Open NYPd Chart Scale

The Visionary Mind of Travis Willingham: Architect of Mythic Storytelling

Uncovering the Hidden Stories: The Origins and Meanings Behind Powerful Name Roots

Carolina North Time: Unlocking the Rhythm That Defines the Carolinas’ Mobilized Morning

