Hurricane Rafael 2025: A Raging Force Forecast to Slam the Caribbean and East Coast
Hurricane Rafael 2025: A Raging Force Forecast to Slam the Caribbean and East Coast
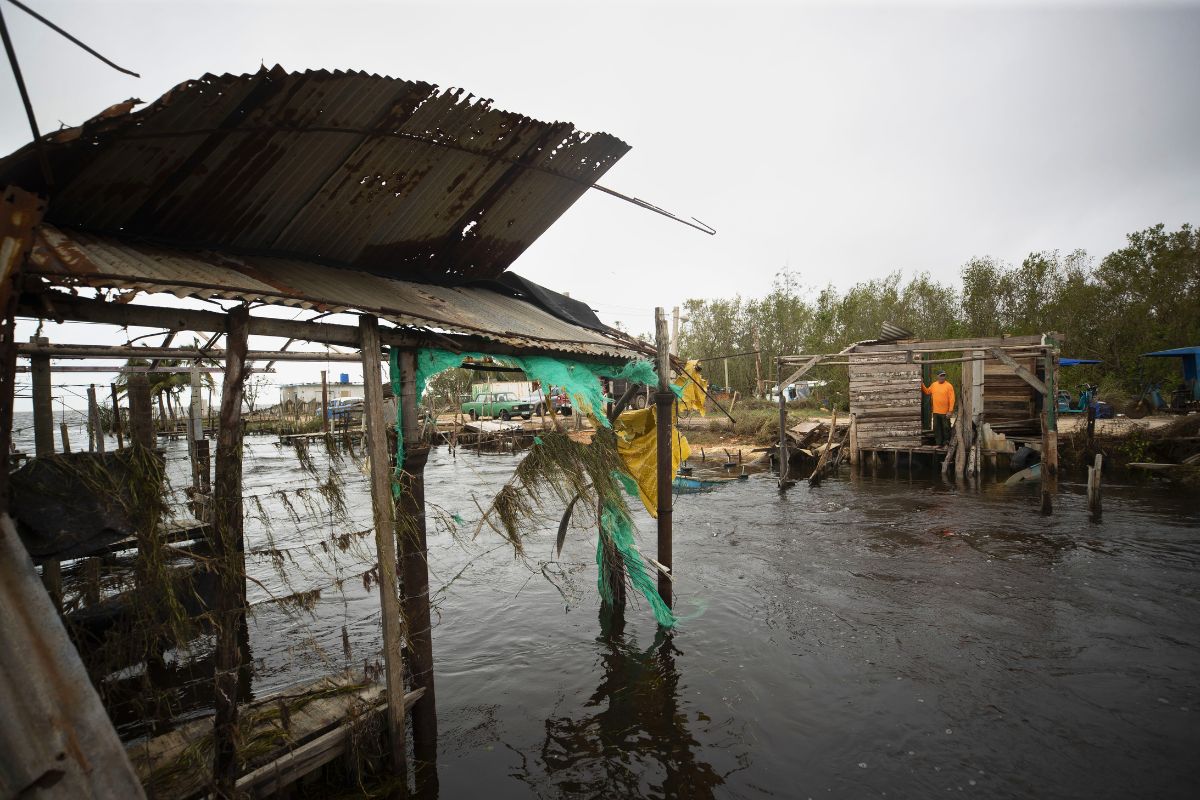
When Hurricane Rafael loomed over the eastern Atlantic in early October 2025, meteorologists sounding alarms found themselves tracking one of the most powerful and anticipated storms of the Atlantic Basin’s active season. With sustained winds exceeding 130 mph and a trajectory threatening populated coastlines, Rafael emerged not just as a weather event but as a significant challenge demanding urgent preparedness from emergency managers, coastal communities, and federal agencies. As rainy bands stretched from the Greater Antilles toward the Mid-Atlantic, forecasters warned of life-threatening storm surge, catastrophic flooding, and widespread infrastructure damage.
This article unpacks Rafael’s formation, projected path, impact zones, and the multi-layered response effort shaping its legacy in 2025.
How Hurricane Rafael Formed and Intensified
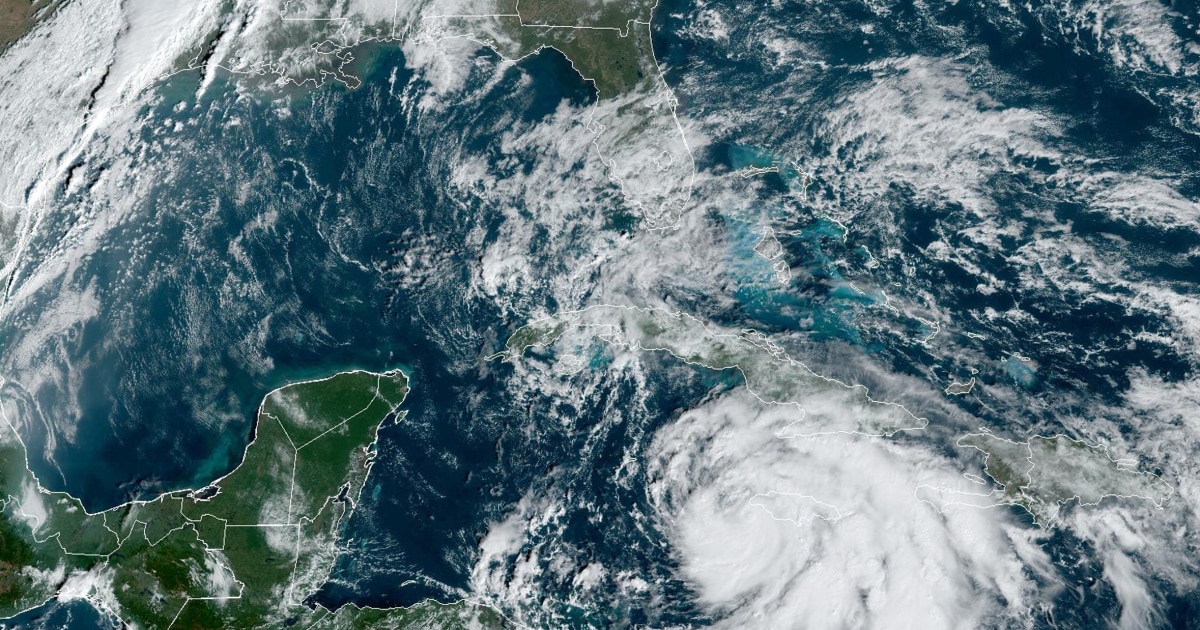
Tracing its origins to a tropical wave east of the Cape Verde Islands, Hurricane Rafael rapidly organized under favorable upper-level conditions and unusually warm sea surface temperatures—conditions amplified by a developing Atlantic Ocean heat content peak in late summer 2025. By October 3, the system had been classified a Category 5 hurricane, the highest rank on the Saffir-Simpson scale, with a compact but exceptionally organized core featuring a well-defined eye and symmetrical rainbands.The storm’s intensity peaks were no accident. Enhanced satellite data revealed an eye cooling signature and rapid isobaric drop—key indicators of explosive deepening. According to the National Hurricane Center (NHC), Rafael’s pressurized core dropped nearly 25 millibars in 24 hours, a hallmark of rapid intensification fueled by ocean heat flux exceeding 1.5×10²² joules per day—among the highest rates observed in recent Atlantic seasons.
Meteorologists noted that Rafael’s formation coincided with a transition phase in the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (AMO), a climate pattern linked to increased hurricane frequency and strength. “The combination of cooler wind shear and record-warm SSTs created a near-ideal nursery,” said Dr. Elena Torres, a senior tropical meteorologist with the NHC.
“We saw an almost textbook case of environmental support aligning perfectly with internal storm dynamics.”
Tracking Rafael: From Blizzard-Like Warmth to East Coast Horror
By October 5, Hurricane Rafael had weakened slightly to Category 4 but remained staggeringly potent. Satellite imagery revealed a vast, wind-driven system with rainbands stretching over 700 kilometers from the Windward Islands northward. The storm’s forward speed slowed as it approached the Leeward Islands, prolonging



Related Post

Hurricane Rafael 2025: How Scientists Are Predicting Its Path with Unprecedented Precision
Fixing Roblox Connection Errors: A Comprehensive Guide to Restore Smooth Gameplay

Unlock Math Mastery: How Ti Nspire Online Transforms Classroom Learning

Unmasking The Truth: What Is Homelander's Public Image?

